The Most Common Enneagram Type: Global Statistics, Rankings, and Rarity
January 30, 2026 | By Seraphina Croft
Understanding where you fit in the Enneagram spectrum is more than just a numbers game—it’s about context. Many people ask, "Am I normal?" when they see their enneagram test results, while others secretly hope to be the rarest of them all.
This guide breaks down the latest global statistics on Enneagram population distribution. You will discover which types dominate society, which ones are surprisingly scarce, and why the numbers might not tell the whole story.
Beyond the rankings, we will explore how gender influences these stats and why self-reporting often skews the data. Most importantly, you will learn why relying on averages can lead to mistyping and how to find your true core number.
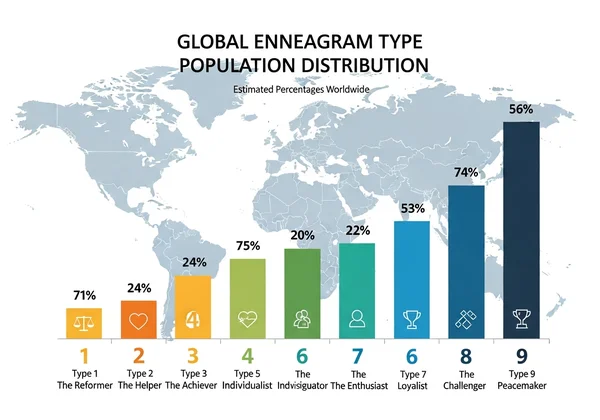
The Verdict: Which Enneagram Type Is Statistically the Most Common?
If you are looking for the crowd favorite, the data points clearly in one direction. While exact percentages vary between studies, the consensus is strong: the Type 9 Peacemaker is the most common Enneagram type in the general population.
This makes sense when you consider the core motivation of a Nine: the desire for harmony and conflict avoidance. In many cultures, these traits are highly adaptable, allowing Nines to blend in seamlessly.
Close on their heels is the Type 6 Loyalist. Together, these two types make up a significant portion of society, often accounting for nearly 25-30% of people combined.
The Peacemaker (Type 9): Why They Top the Lists
Type 9s are the social glue of the world. Their ability to see all perspectives makes them incredibly common because they often prioritize group cohesion over individual assertion.
This high prevalence might also be influenced by how Nines self-report. Because they often merge with others' opinions, a Nine might mistype themselves as a Helper (2) or an Achiever (3), yet they still dominate the raw data as the most frequent result.
The Loyalist (Type 6): The Close Second
Type 6 is the other giant in population statistics. Loyalists are focused on security, community, and preparedness. In a world that values safety and structure, the Type 6 personality thrives.
It is worth noting that 6s and 9s share a "Triangle" connection in the Enneagram symbol (along with Type 3). This internal link often means people fluctuate between these behaviors, further boosting their representation in surveys.
Why Statistics Vary Between Studies
You might see different rankings depending on where you look. This happens because most Enneagram data comes from people taking online tests.
- Self-Selection Bias: People who take personality tests are often introspection-seekers (like Type 4s or 5s), which can artificially inflate their numbers in smaller samples.
- Cultural Differences: A study in Japan might show different results than one in the United States due to cultural values around collectivism versus individualism.
However, even with these variables, Type 9 and Type 6 consistently remain at the top of the most common enneagram lists.
The Full Rarity Scale: Ranking Enneagram Types from Common to Rare
Knowing the most common type is just the start. Where does the rest of the population fall? We can group the nine types into three distinct tiers based on their frequency.
The "Common Core" (Types 9, 6, 3)
These three types are the bedrock of society. You likely encounter them every day in your workplace, family, and friend circles.
- Type 9 (Peacemaker): The receptive mediator.
- Type 6 (Loyalist): The committed security-seeker.
- Type 3 (Achiever): The adaptable, success-oriented performer.
Type 3s round out this group. Their drive for success and adaptability allows them to thrive in modern, goal-oriented cultures, making them a very visible part of the population.
The "Uncommon Middle" (Types 2, 7, 1)
These types are frequently seen but not dominant. They add specific flavors to social dynamics without being overwhelming in number.
- Type 2 (Helper): Warm and giving, often found in caregiving roles.
- Type 7 (Enthusiast): Spontaneous and scattered, bringing energy to the group.
- Type 1 (Reformer): Principled and orderly, often holding systems together.
The "Rare Gems" (Types 5, 4, 8)
If you identify with one of these, you are statistically in the minority. These types often feel like "outsiders" or misunderstood, which aligns with their low numbers.
- Type 5 (Investigator): The intense, cerebral observer.
- Type 8 (Challenger): The powerful, assertive protector.
- Type 4 (Individualist): The expressive, dramatic romantic.
Type 4 is widely considered the rarest Enneagram type. Estimates often place them at fewer than 10-15% of the population. Their core desire to be unique is ironically supported by the fact that they are, statistically, the most unique.
Gender Breakdown: Most Common Enneagram Types for Females vs. Males
When we split the data by gender, the enneagram population distribution shifts in interesting ways. While biology doesn't dictate personality, socialization and cultural expectations play a huge role in how men and women identify.
Top Types Among Women (The Helper Influence)
For women, Type 2 (The Helper) jumps significantly in rankings. This aligns with societal pressure on women to be nurturing, relational, and self-sacrificing.
- Most Common: Type 2, Type 9, Type 6.
- Rare: Type 8 and Type 5.
It is rare to find female Type 8s in high numbers. Women with assertive, anger-forward energy are often socially conditioned to suppress it, leading many to mistype as 2s or 6s to fit in.
Top Types Among Men (The Challenger Influence)
For men, the Type 9 remains the most common, but Type 8 (The Challenger) appears much more frequently than in women.
- Most Common: Type 9, Type 5, Type 3.
- Rare: Type 2 and Type 4.
Men are often discouraged from showing vulnerability (Type 4) or overt neediness (Type 2). Consequently, a male Type 2 might mistype as a 9 or a 6 to appear more stoic or "neutral."
The "Mistype Matrix": Which Enneagram Type Is Hardest to Identify?
Here is the catch with all these statistics: they rely on people knowing their type accurately. Unfortunately, mistyping is rampant. If you are basing your identity solely on which types are "common," you might be led astray.
Why Type 9s and 6s Are Often Misidentified
Type 9s and 6s are the hardest enneagram types to identify correctly because they are "adaptation" types.
- The Chameleon Effect: A Type 9 can merge with the energy of a Type 3 partner or a Type 8 boss. They might take a test thinking, "I am ambitious," when they are actually just mirroring their environment.
- The Anxiety Factor: A Type 6 reacts to fear. Sometimes they fight it (looking like an 8), and sometimes they follow rules (looking like a 1).
This fluidity means the "most common" statistics might be slightly inflated by people who haven't yet found their core motivation.
Social Desirability Bias: Answering Who We Want to Be
We all want to be seen in a good light. This bias skews data heavily.
- Few people want to admit they are manipulative (unhealthy Type 2) or fearful (unhealthy Type 6).
- Many people want to be seen as helpful (Type 2) or strong (Type 8).
If you took a test and answered based on your "ideal self" rather than your "real self," your result—and the global stats—might be off.
Stop Guessing: Discover Your True Core Type
Statistics are fascinating, but they are just averages. You are not a statistic. Whether you fall into the 20% of Type 9s or the 2% of Type 4s, your journey is about understanding your specific patterns, not fitting into a demographic box.
Why Statistics Are Just Averages (And You Are Unique)
Knowing that Type 6 is common doesn't tell you why you feel anxious at night. Knowing Type 4 is rare doesn't explain why you feel misunderstood in your relationship.
True self-discovery goes beyond probability. It requires looking at your core fears and motivations, which are often hidden beneath layers of social conditioning.
Take the EnneagramTest.me Assessment
If you are unsure where you land—or if you suspect you might be one of the "mistyped" majority—it is helpful to use a structured tool to cut through the noise.
Our platform offers a dedicated assessment designed to look past behavioral traits and identify core motivations. You can try the enneagram test on our site to get a baseline.
For those who want deeper clarity, our AI-powered report analyzes your unique blend of wings and instincts, offering a personalized roadmap that goes far beyond a simple number.

The MBTI Connection: Most Common Enneagrams for Each Personality
A massive area of interest is how the Enneagram overlaps with the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI). While they are different systems, strong correlations exist. This section covers the most common enneagram for mbti types.
Common Pairings for Introverts (INTJ, INFJ, INTP)
Introverts often align with the "Withdrawn" or "Competency" stances in the Enneagram.
- INTJ: Most commonly Type 5 (The Investigator) or Type 1 (The Reformer). It is rare to see an INTJ Type 2.
- INFJ: Often correlates with Type 4 (The Individualist) or Type 2 (The Helper). The "Rare" INFJ matches the "Rare" Type 4 perfectly.
- INTP: Heavily dominated by Type 5. The thirst for knowledge is the defining trait for both.
Common Pairings for Extroverts (ENFP, ENTJ, ESFP)
Extroverts tend to cluster around the assertive and image-conscious types.
- ENFP: The classic Type 7 (The Enthusiast). Their shared love for possibility makes this a near-perfect match.
- ENTJ: Almost exclusively Type 8 (The Challenger) or Type 3 (The Achiever). They lead with command and efficiency.
- ESFP: Frequently Type 7 or Type 2. They bring the party and the heart.
Can You Be a Rare Combination?
Yes, and these are often the most dynamic personalities.
Imagine an ENTP Type 2. This person would be intellectually combative yet deeply caring—a confusing but fascinating mix. Or consider an ISFJ Type 8, a quiet protector who suddenly explodes with assertion when their family is threatened.
If your MBTI and Enneagram don't "match" the charts, don't worry. You might just be a rare combination that requires a more nuanced approach to understand.
Embracing Your Type (Common or Rare)
Whether you are a Type 9 blending into the crowd or a Type 4 standing apart, your value isn't determined by your rarity. Being "common" means you have a natural ability to relate to a huge portion of humanity. Being "rare" means you offer a perspective the world often misses.
The goal of the Enneagram isn't to be special; it's to be aware.
If you are ready to move past the guessing game, check your traits with our free personality assessment and start your journey toward self-awareness today.
Frequently Asked Questions about Enneagram Stats
Is one Enneagram type better than another?
No, no type is inherently better or worse. Each type has healthy, average, and unhealthy levels of development. A healthy Type 6 is courageous and loyal, while an unhealthy Type 6 is paranoid. The goal is growth, not changing your number.
Does Enneagram type distribution change with age?
Your core Enneagram type does not change, but how you express it does. As people age, they often become more balanced. A young Type 8 might be aggressive, while an older Type 8 might use their strength to mentor others. This can make older populations "look" different in stats, but their core motivation remains the same.
Do cultural factors influence which types are most common?
Absolutely. Western individualistic cultures (like the US) might report higher numbers of Type 3s and 8s because those traits are rewarded. Eastern collectivist cultures might see higher reporting of Type 9s and 6s because group harmony is valued over individual distinction.
Why are Type 4s considered so rare?
Type 4s are focused on their internal emotional landscape and authenticity. This level of introspection is energy-intensive and less focused on biological survival (like the safety-seeking 6) or social cohesion (like the 9). From an evolutionary standpoint, having too many intense individualists might have been less advantageous for tribal survival, keeping their numbers naturally lower.
What is the most common Enneagram type for INTJ?
The most common Enneagram for an INTJ is Type 5 (The Investigator). Both systems prioritize logic, competence, and objectivity. Type 1 (The Reformer) is a close second due to the shared desire for structure and correctness.
Can I try a test to confirm my type?
Yes, using a validated assessment is the best way to confirm your suspicions. You can try the most common enneagram online test on our site to get a detailed breakdown of your personality profile.